Cube
Overview[edit]
Settings:
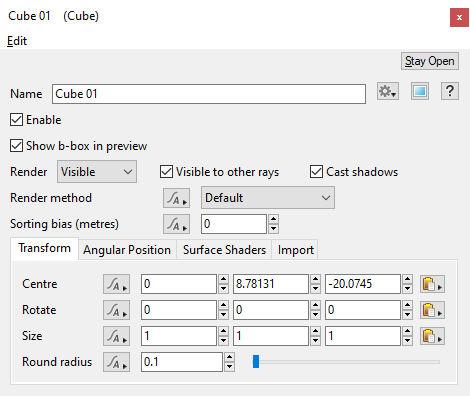
- Name: This setting allows you to apply a descriptive name to the node, which can be helpful when using multiple Cube nodes in a project.
- Enable: When checked, the node is active and the Cube object will appear in the scene with the settings below applied to its surface. When unchecked, the node is ignored.
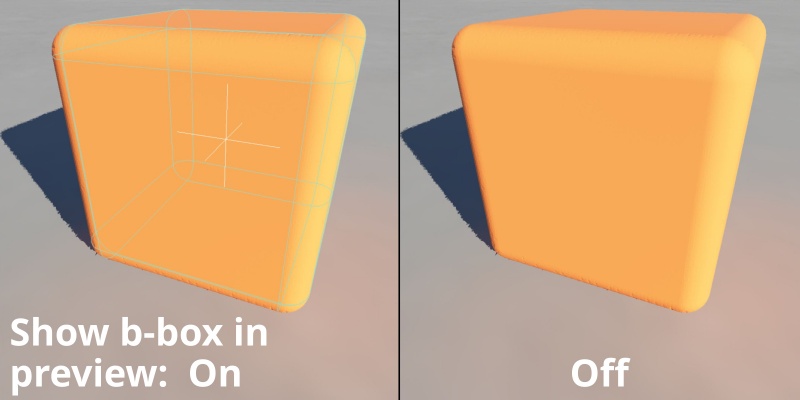
- Show b-box in preview: When checked, the bounding box of the cube shape will be displayed in 3D Preview.
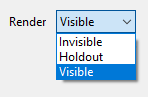
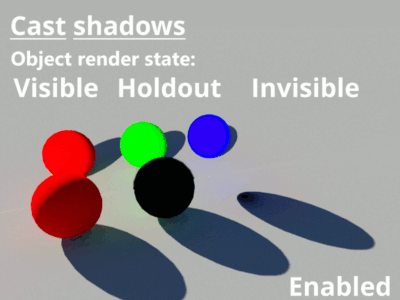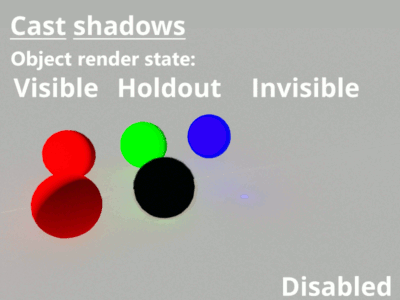
- Render: An object's render state can be set to Visible, Invisible or Holdout. When set to Holdout, an object is visible in the rendered image as a black shape with an alpha value of zero. When using render layers the object's render state is combined with the group visibility parameter to determine its least visible setting. Invisible is less visible than Holdout, which is less visible than Visible.
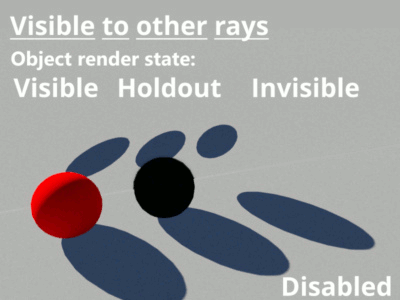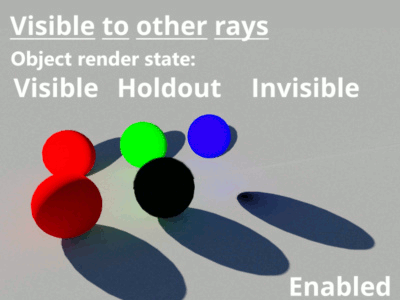
- Visible to other rays: When enabled, the cube object will be taken into account by all the rays determined by the renderer including those from the camera, direct and indirect lighting, etc. In the example below, a 100% reflective 3D object has been placed behind three coloured spheres in order to mirror the effect of the calculated rays.
- Cast shadow: When checked, the cube object will cast shadows.
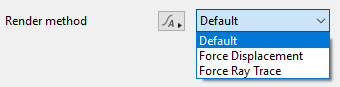
- Render method: This popup has three options.
Default: Ray Tracing is the default rendering method for an object. Typically it results in higher quality and faster rendering. When displacement is applied to a 3D object the render method should be changed to Force Displacement. When the object's render method is set to Default, the object is rendered according to the Ray trace objects setting in the render node.
Force Displacement: When enabled for the cube object, its surfaces will be subdivided into micropolygons at render time, which allows the 3D geometry to be displaced correctly but at the expense of slightly longer render times. It is useful when you have some objects you want to render with displacement but you don't want to change how all the rest of your objects are rendered, i.e. Ray traced.
Force Ray Trace: When enabled for the cube object, its surfaces will be ray traced at render time, even if Ray trace objects is disabled in the Renderer settings. This can be useful when Ray trace objects is disabled in the Renderer in order for other 3D objects to use displacement, but you want this object to use ray tracing for the highest quality rendering and it has not been displaced.
- Sorting bias (metres): This setting gives you control over the order in which objects are rendered when using the micropolygon renderer. This does not apply to objects being rendered with the ray tracer. A large positive value, e.g. 10,000,000 (or 1e7) will usually force the object to render first. A large negative value, e.g. -10,000,000 (or -1e7) will usually force the object to render last, or after the terrain. This can be useful when rendering large objects with displacement, such as a lake object that lies mostly below the displaced terrain. By setting the lake object’s Sorting bias (metres) value to something like -10,000,000 forces it to render after the terrain.
Transform Tab[edit]
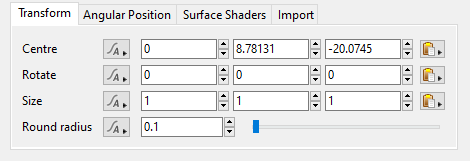
- Centre: This setting allows you to reposition the cube object by entering values in the XYZ input fields. The origin, or pivot point, of the cube is its exact center. Therefore, in order for the bottom of the cube, with Size values of 1,1,1, to rest on the ground, the cube’s Centre Y axis value would need to be set to 0.5.
- Rotate: This setting allows you to rotate the cube object around its origin, or pivot point, which is located at the exact center of the cube..
- Size: This setting allows you to scale the cube independently along each axis.
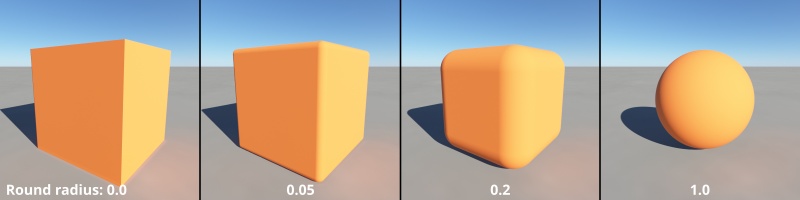
- Round radius: This setting allows you to smooth the edges of the cube. A value of 0 results in sharp edges. Increasing the value eventually results in a sphere shaped cube.
Angular Position Tab[edit]
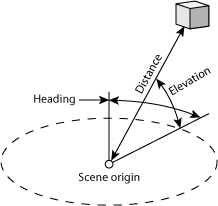
This tab has settings which use angles and distance to set the position of the cube object relative to the scene origin. These settings are an alternative to using the Translate setting in the Transform tab. The diagram below shows how all the parameters relate to each other and the origin.
- Heading: This angle sets the rotation of the cube object around the scene origin, in the XY plane, increasing as you turn clockwise.
- Elevation: This angle sets the vertical part of the position. You could think of it as the angle above or below the horizon. 90 is straight up, -90 is straight down.
- Distance: This sets the distance of the cube object from the origin, in metres.
Surface Shaders Tab[edit]
This tab lets you assign a surface shader to texture the cube object.
- Surface shader: Use this setting to assign a surface shader or function nodes to the cube object. The examples below were created by Terragen users and can be found under the File Sharing section on the Planetside Software forums.
- Displacement tolerance: If you find that rough or spikey surfaces are showing problems at bucket edges, for example spikes having cut off tops, or gaps in ray traced shadows then increasing this value may help. However this can greatly increase render times. Relatively flat surfaces may render more quickly with smaller values. The default value is 1. However this is an advanced setting and you should not change it unless you have a specific problem you need to address. If you are having problems try starting with 2 and then increase it by small increments until they're resolved. A value of 4 would be considered a high value.
Import Tab[edit]
These parameters apply to .chan/.mov and FBX import.
- Import offset: This setting allows you to offset the positions imported from the file. As an example, you might want the positions imported from the file to be moved 10 metres in the X direction. To do that enter 10 for the X coordinate and import the file.
- Import scale: You can use this setting to scale values imported from the file.
- Import Chan file: This param specifies the file to be imported. When you a choose a new file you will be prompted to import the file. If you choose not to import it immediately you can click the Import chan File button to perform the import.
A single object or device in the node network which generates or modifies data and may accept input data or create output data or both, depending on its function. Nodes usually have their own settings which control the data they create or how they modify data passing through them. Nodes are connected together in a network to perform work in a network-based user interface. In Terragen 2 nodes are connected together to describe a scene.
The bounding box is a box which surrounds (or bounds) an object or shader. This box shows the maximum extents of the item inside it. Sometimes abbreviated as "b-box".
A parameter is an individual setting in a node parameter view which controls some aspect of the node.
Literally, to change the position of something. In graphics terminology to displace a surface is to modify its geometric (3D) structure using reference data of some kind. For example, a grayscale image might be taken as input, with black areas indicating no displacement of the surface, and white indicating maximum displacement. In Terragen 2 displacement is used to create all terrain by taking heightfield or procedural data as input and using it to displace the normally flat sphere of the planet.
A shader is a program or set of instructions used in 3D computer graphics to determine the final surface properties of an object or image. This can include arbitrarily complex descriptions of light absorption and diffusion, texture mapping, reflection and refraction, shadowing, surface displacement and post-processing effects. In Terragen 2 shaders are used to construct and modify almost every element of a scene.
When Terragen renders, it divides the image up into buckets or tiles. Each bucket is rendered separately, allowing multiple buckets to be rendered at once. It also allows memory to be used more efficiently.