Cloud Layer v3
Redirect page
Redirect to:
Contents
Overview[edit]
Main Tab[edit]
Settings:
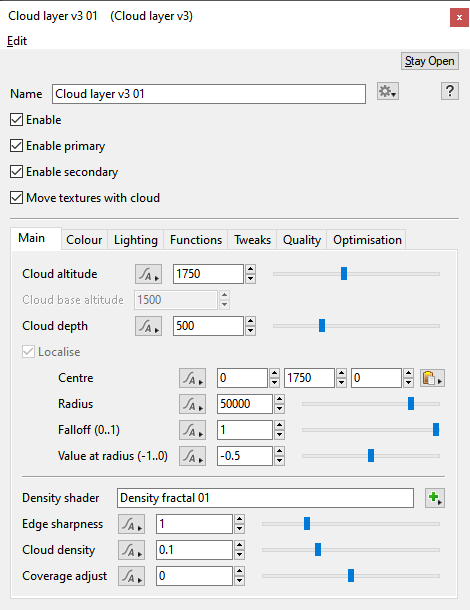
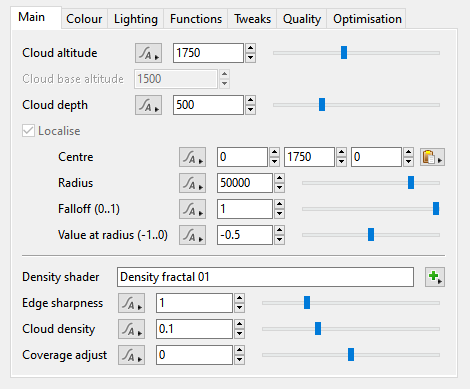
- Cloud altitude: This setting defines the mid-point of the Cloud Layer v3 between its base and top. It is also the same value as the “Y” component of the Centre setting, and changing either setting automatically updated the other.
- Cloud base altitude: This setting is for display purposes only and can not be edited. It mirrors the “Cloud base (min)” display readout beneath the Cloud Node list. Changing the “Cloud altitude”, “Cloud depth” or “Centre” settings will cause this setting to update automatically.
- Cloud depth: This setting defines the height, or depth, of the Cloud Layer v3. Half of its value extends below the “Cloud altitude” and half above. For example, if the "Cloud depth" and "Cloud altitude" values were 1,000 metres, then the Cloud layer v3 would extend from 500 metres to 1,500 metres in altitude.
- Localise: This setting is enabled by default and can not be edited because Cloud Layer v3 clouds require a localised voxel buffer to calculate light scattering.
- Centre: This setting is the position coordinates of the Cloud Layer v3 within the project. The “Y” component value is the same as the "Cloud altitude" and changing either setting will automatically update the other.
- Radius: This setting defines the maximum extent of the Cloud Layer v3.
- Falloff (0..1): This setting controls the density of the cloud from its centre to the edge of the localisation sphere. A curve is applied to fade out the cloud as it approaches the edge. A value of 0 means there is no falloff and the clouds will have a hard edge at the sphere radius. Larger values make the clouds fade out more towards the edge of the sphere.
- Value at radius (-1..0): This setting controls opacity of the clouds at the edge of the radius.
- Density shader: The shader or function assigned to this setting provides the Cloud Layer v3 with its basic shape or pattern. By default a Density fractal shader is automatically assigned when a new Cloud Layer v3 is created. To change the basic shape of the clouds you need to modify the assigned shader or function.
- Edge sharpness:
- Cloud density: Along with "Edge sharpness" this setting controls the transparency or opaqueness of the clouds within the cloud layer. Low values make the clouds look thin and let more light pass through them. Higher values make the clouds look thicker and denser, as well as darker because less light passes through them. Generally speaking we recommend using the "Cloud density setting" because the automatic sampling adjustments that derive from the "Ray-marching quality" are more strongly influenced by "Cloud density" than by "Edge sharpness". In other words, if you set "Cloud density" very high, the render quality will adjust accordingly to keep the noise levels the same, but if you do this with "Edge sharpness" it will not increase sampling to the same degree, meaning that you might have to increase the "Ray-marching quality" much higher than is typical for most scenes.
- Coverage adjust: This setting controls the amount of clouds within the cloud layer. Low values reduce the amount of individual clouds and increase the amount of empty space between them. Increasing the value fills up the area with more individual clouds.
Colour Tab[edit]
Lighting Tab[edit]
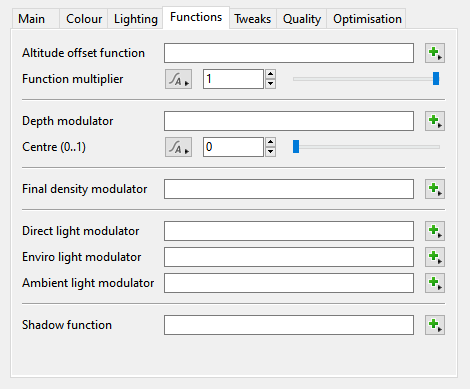
Functions Tab[edit]
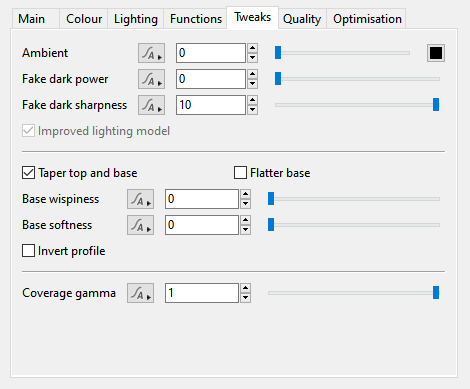
Tweaks Tab[edit]
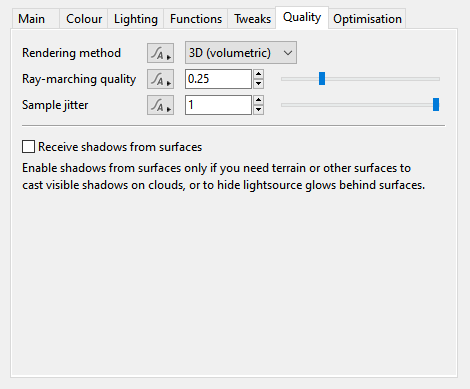
Quality Tab[edit]
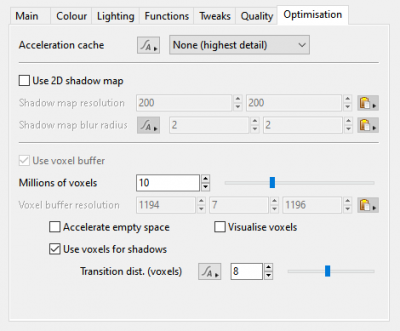
Optimisation Tab[edit]
A shader is a program or set of instructions used in 3D computer graphics to determine the final surface properties of an object or image. This can include arbitrarily complex descriptions of light absorption and diffusion, texture mapping, reflection and refraction, shadowing, surface displacement and post-processing effects. In Terragen 2 shaders are used to construct and modify almost every element of a scene.